Competencies of SAP consultants in Poland in 2025

In September 2025, SAP celebrates its 30th anniversary in Poland. Although the SAP labor market is relatively young, it features a well-developed segment of mid-level specialists and a growing group of seniors. It has already cultivated a wide circle of experts – 1/5 of specialists have more than 15 years of experience, which ensures a pool of independent professionals with deep system understanding. These consultants and developers understand how earlier versions of the system worked, helping them propose better-tailored solutions in the context of the transformation to S/4HANA.
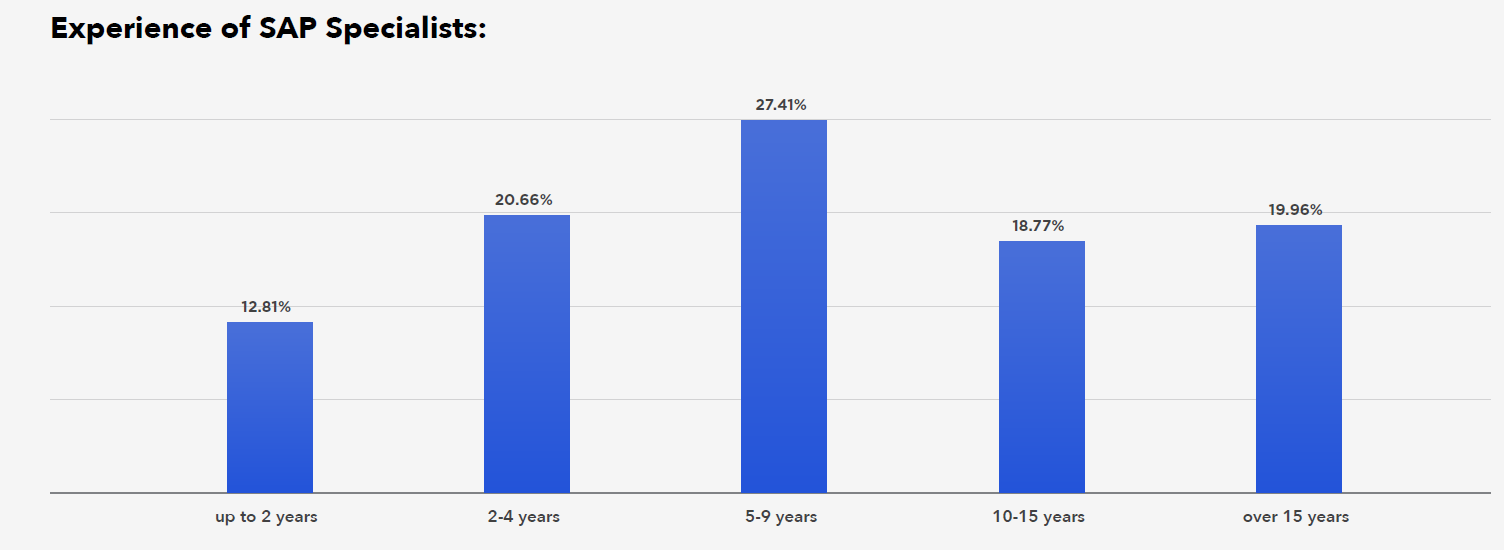
At the same time, SAP is attracting new employees – 1/3 of the community consists of people at entry level (up to 2 years) and junior employees (2-4 years).
Contracts vs Permanent Employment
SAP streamlines business processes by systematizing them while utilizing a common database. It enables companies to maintain comprehensive records and monitor activities across multiple areas. Effective system implementation requires cooperation between experienced SAP consultants and business and internal experts.
These two environments are also visible in the job market – advisory consultants handle implementations, while internal experts, thanks to their organizational knowledge, play a key role as their partners. As experience grows, SAP specialists increasingly prefer to work on individual contracts – both in consulting firms and as freelancers.
Consultants and developers working on contracts carry out implementations, migrations, and system optimizations for various clients, all of which requires flexibility, broad technological knowledge, and frequent changes in the work environment. Meanwhile, those permanently employed in companies using SAP tend to focus on maintaining, developing, and customizing the system for internal business processes, ensuring its stability and optimization.
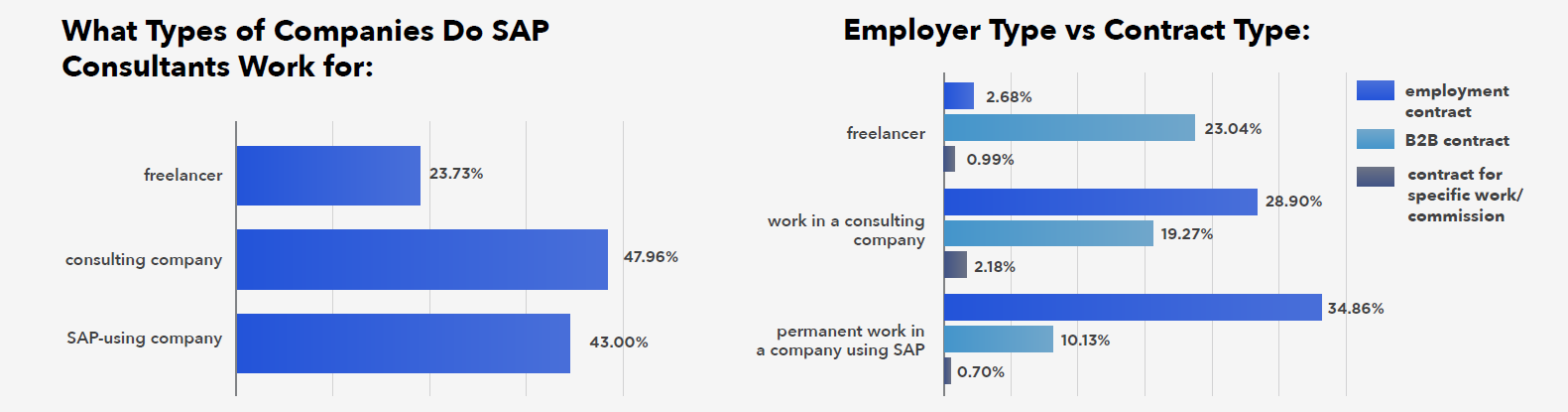
However, these are not hermetic environments. 13% of SAP specialists permanently employed in companies using SAP also work as freelancers, as do 16% of specialists from consulting firms. As their experience grows, permanent specialists transition to contracts, while some contractors choose stability and permanent employment at certain points in their careers.
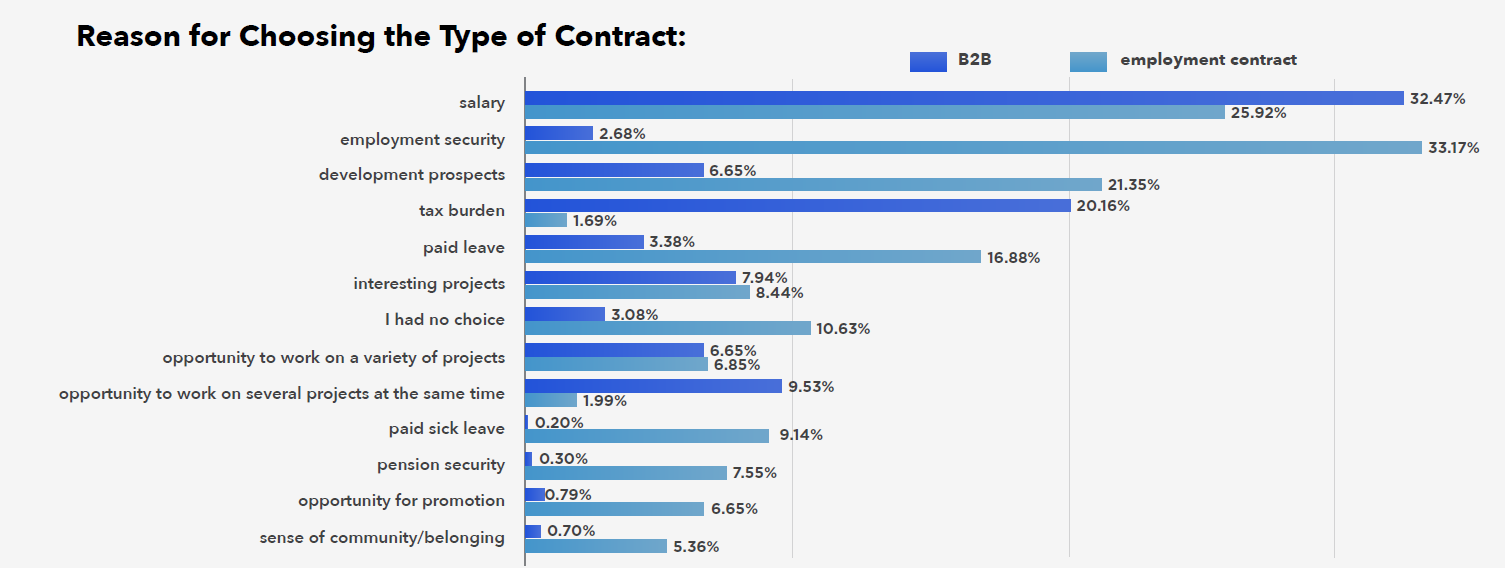
The choice of career path influences the form of employment – most specialists working for a single company choose permanent positions, while (B2B) contracts dominate in consulting. People opting for employment contracts are usually motivated by job stability, the desire to develop within one organization, and the traditional advantages of this form of employment, such as paid holidays and pension security. For B2B, key factors include higher earnings, greater flexibility in project selection, the possibility of working for multiple clients, and gaining broader experience.
Role Structure in SAP
The SAP community is dominated by functional consultants (53%), followed by technical consultants (27%) and developers (23%). Compared to the IT market as a whole, there is a notably high percentage of architects (14%), positions typically filled by experienced functional or technical consultants. Migration to SAP S/4HANA is a significant factor increasing the demand for architects. These projects require individuals capable of critically evaluating solutions proposed by consultants, especially from the perspective of cross-module integration.
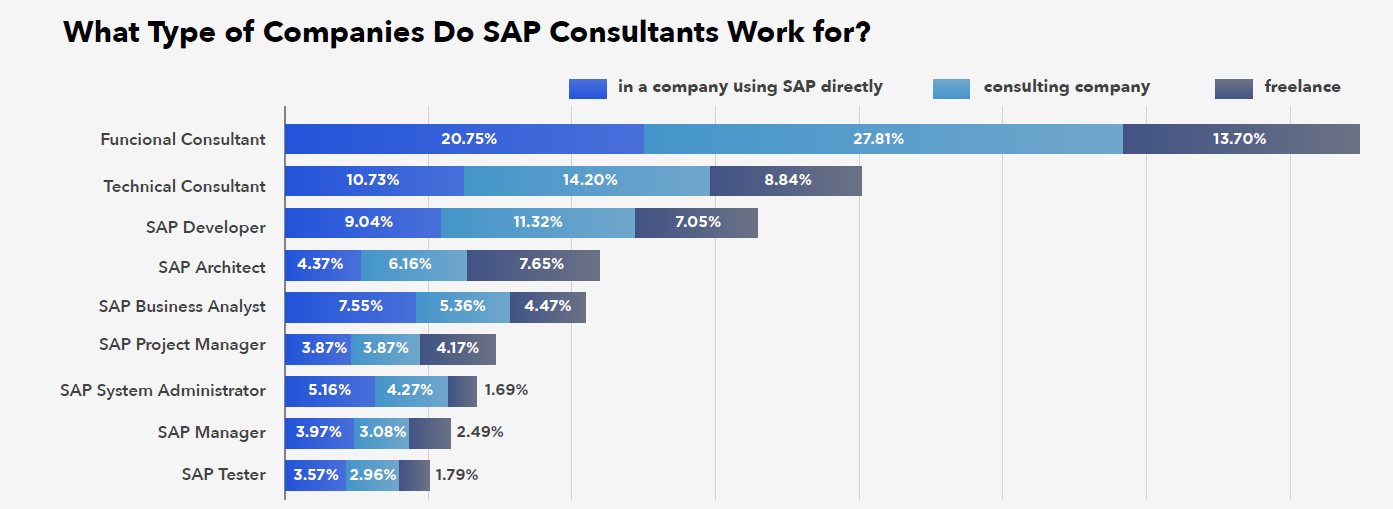
Among SAP architects, the proportion of freelancers is particularly high, reflecting the project-based nature of this role. Administrators and analysts most often work internally for companies using SAP, while the majority of consultants and developers choose consulting firms.
Functional Consultants
Among SAP consultants, the majority consist of specialists in production, sales, supply chain management, and finance. Most companies – regardless of the industry – have processes in these areas, and SAP solutions here are among the most mature on the market and enjoy a good reputation.
In production and sales, the market concentrates around MM (Materials Management) and SD (Sales and Distribution) modules, which dominate business applications. The growing importance of EWM (Extended Warehouse Management) and TM (Transport Management) modules indicates the progressive automation of logistics and transport processes. Meanwhile, the increasing role of PP-DS (Production Planning and Detailed Scheduling) and QM (Quality Management) suggests growing demand for precise production planning and quality control.
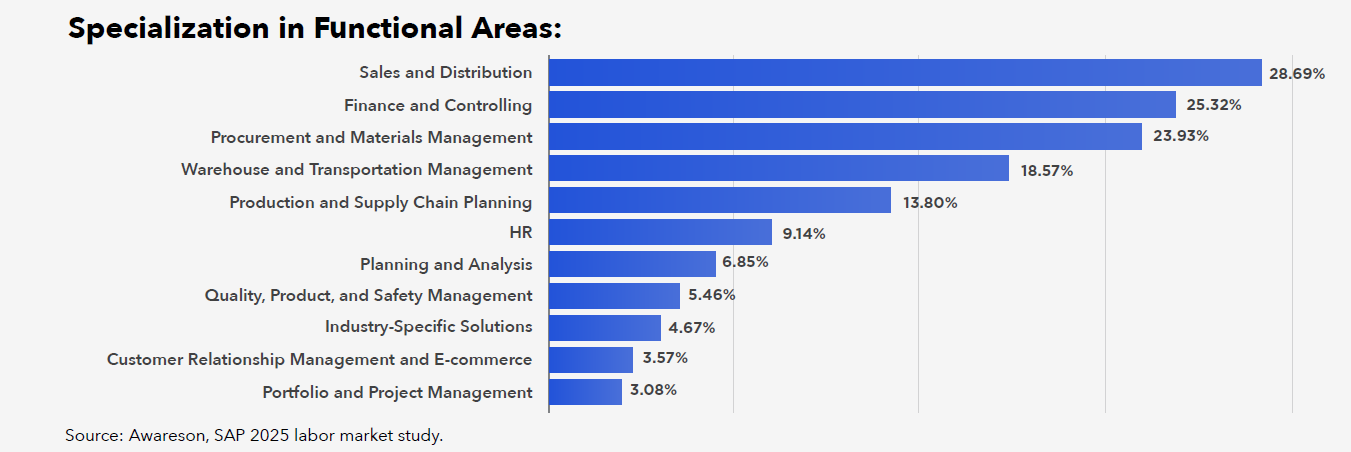
In finance, FI (Finance) and CO (Controlling) modules traditionally dominate. However, there is growing financial maturity in companies – increasing demand for SAP FSCM (Financial Supply Chain Management) and TRM (Treasury and Risk Management) specialists. This stems from the need for better financial management in organisations.
Despite the universality of human resource management processes, SAP solutions in this area are often displaced by alternative systems that can be effectively integrated with SAP (a similar situation applies to CRM). In HR, SuccessFactors is gaining popularity, handling soft aspects of personnel management such as talent management and career planning. This reflects the direction of HR changes in Poland – an increasing focus on data analysis (data-driven HR), employee development, skills improvement and reskilling, as well as retention strategies in response to growing turnover in the labour market and the lack of appropriately qualified employees.
Technical Areas of SAP
Technical specialists are most often developers. Programming in SAP remains a key technical area, with ABAP being the dominant technology (87.83%). However, the importance of Fiori/UI5 (34.12%) is growing, indicating increased demand for a modern, intuitive user interface (SAP Fiori).
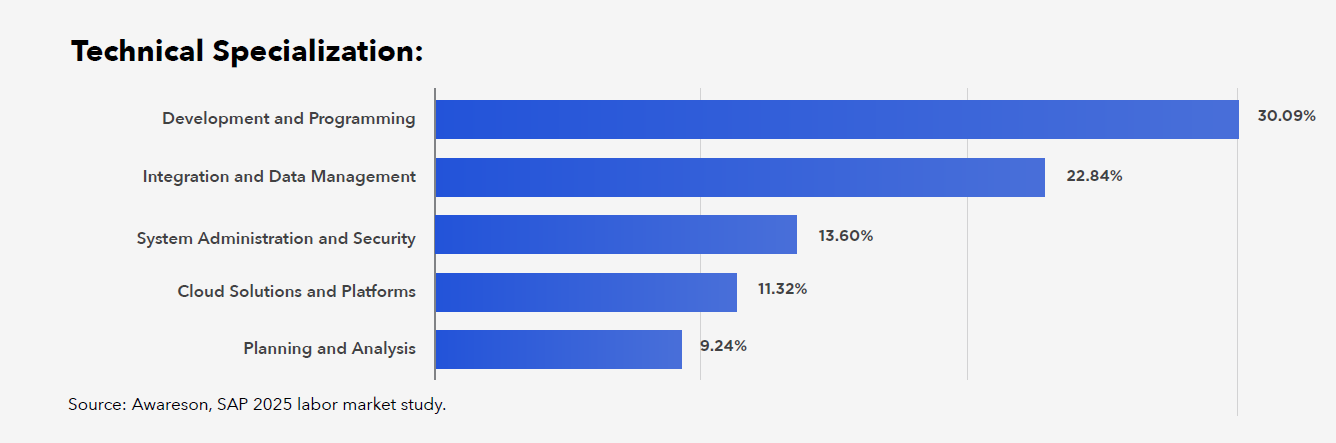
Data modelling (CDS, SQLScript – 39.76%) and OData are crucial for integration with S/4HANA and modern applications. Employers are looking for developers who can combine classic ABAP with new UI technologies and cloud solutions.
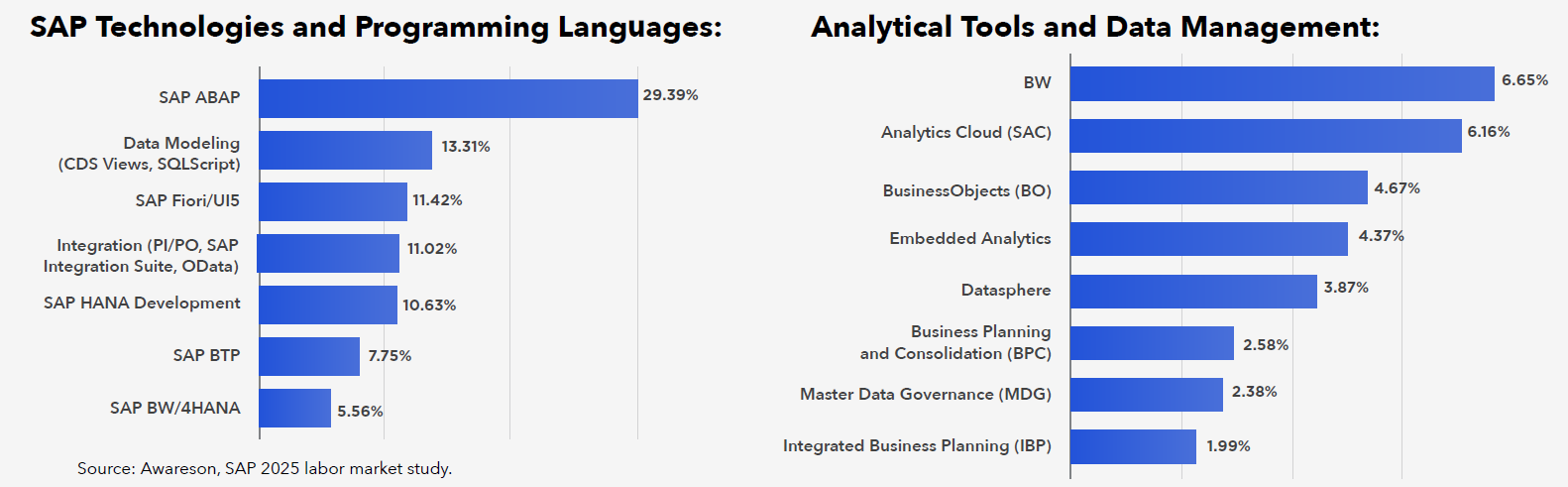
SAP Integration Suite and BTP (23.15%) are gradually replacing PI/PO (32.94%), and MDG (Master Data Governance) boosts control over data. Companies are focusing on automation and centralized data management, which is increasing demand for integration specialists.
SAP BTP and SAP Cloud Platform are gaining in importance, enabling extensions of SAP systems and integration with external applications. And candidates who can achieve this are increasingly scarce in the market. Companies are looking for specialists who can combine on-premise environments with the cloud, which confirms the growing importance of BTP among developers (23.15%).
SAP BW and Datasphere still play a key role in data warehousing, but SAP Analytics Cloud (SAC) is becoming the standard in real-time reporting and analysis. Automation and the data-driven decision making approach mean that analytics specialists are increasingly sought after.
Place of Work
The largest clusters of SAP specialists are in Mazovia – especially in Warsaw – and Lower Silesia, mainly in Wrocław. International organisations have been investing in these regions for years, and Wrocław’s proximity to the German border is an additional advantage of this location for companies using SAP. This is also an strong point of Poznań’s and Katowice’s.
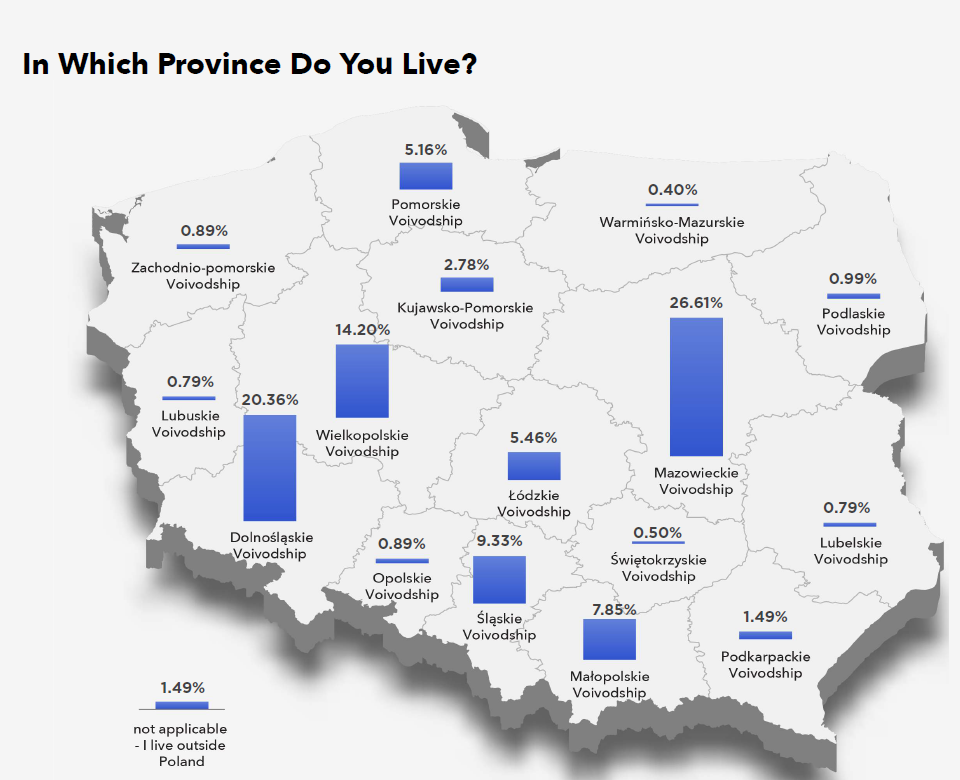
The relatively small talent pool in Kraków, with concurrent interest from foreign investors in this location, may mean that the availability of SAP specialists in this region will gradually decrease.
More than half of SAP specialists still work fully remotely, and the role of hybrid work is growing only slightly (for comparison, in the first Awareson labour market survey in 2023, 81% of respondents worked remotely). SAP specialists report great flexibility – less than 15% “insist” on remote work, and the main reason is usually the distance to their employer’s headquarters.
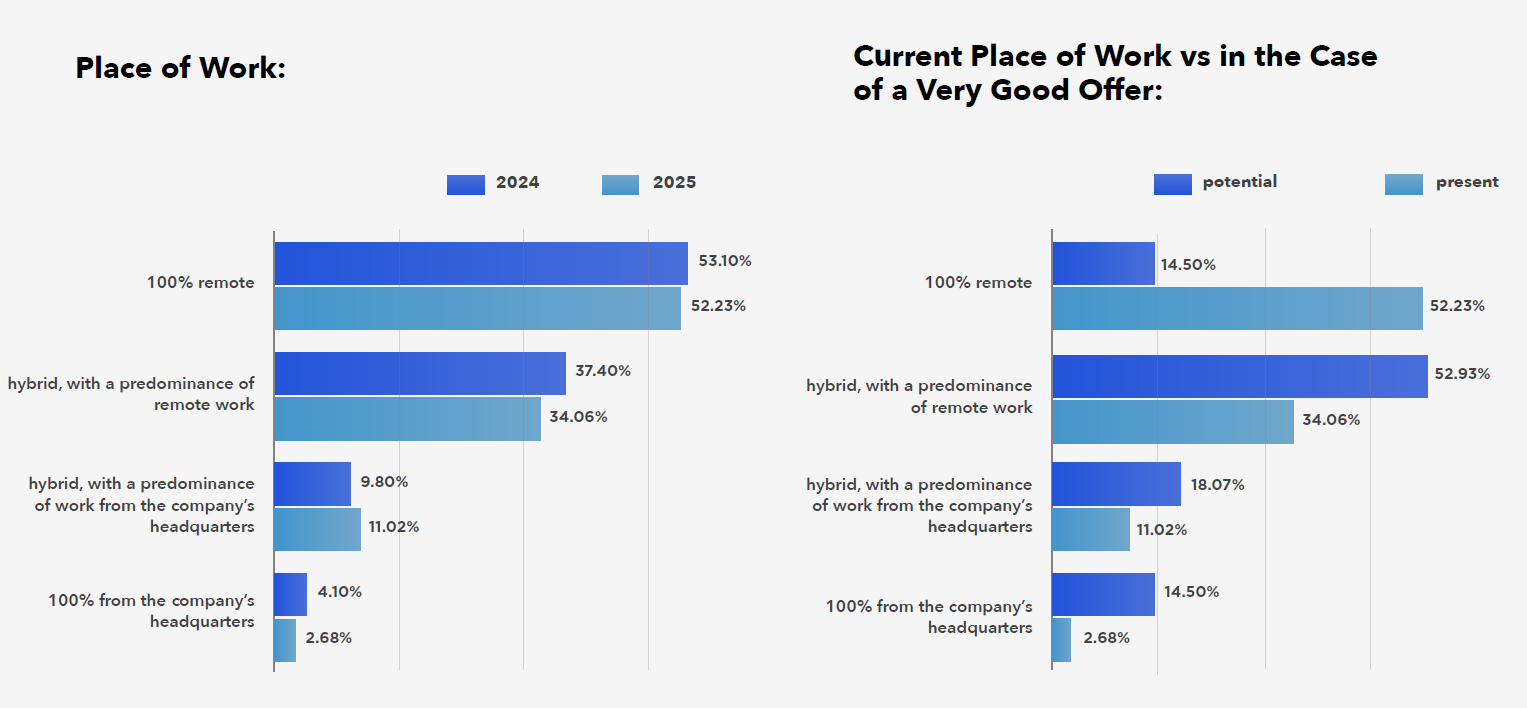
Remote or hybrid work is most often chosen, with a preference for working from home. Junior staff most often come to offices, mainly in search of knowledge.
The hybrid work model is becoming standard, but its implementation comes with challenges. In agglomerations such as Warsaw or Wrocław, the three-day office work model is better adapted to market conditions and specialist availability. In cities with a smaller talent base, e.g. Kraków, it may, however, hinder recruitment and limit access to experts.
Approaches to office-based work differ depending on the person’s experience. Younger professionals willingly work in the office, treating it as a space for learning and knowledge exchange. Experienced experts, especially those on B2B contracts, prefer a limited office presence, focusing on productivity and often working on several projects simultaneously.
To effectively compete for the best SAP specialists, companies must adapt their approach to market realities. Rigid office requirements can limit access to talent, while flexibility makes it easier to acquire and retain it.
The hybrid model should be motivated by real business needs, not formal organisational assumptions. It is therefore worth encouraging highly experienced SAP specialists to visit the office, delegating mentoring roles and responsibilities to them, so that the organization can ensure knowledge transfer and educate new talent, and thus develop senior specialists by drawing on their knowledge and experience.
Aneta Szarow
Senior Key Account Manager at Awareson
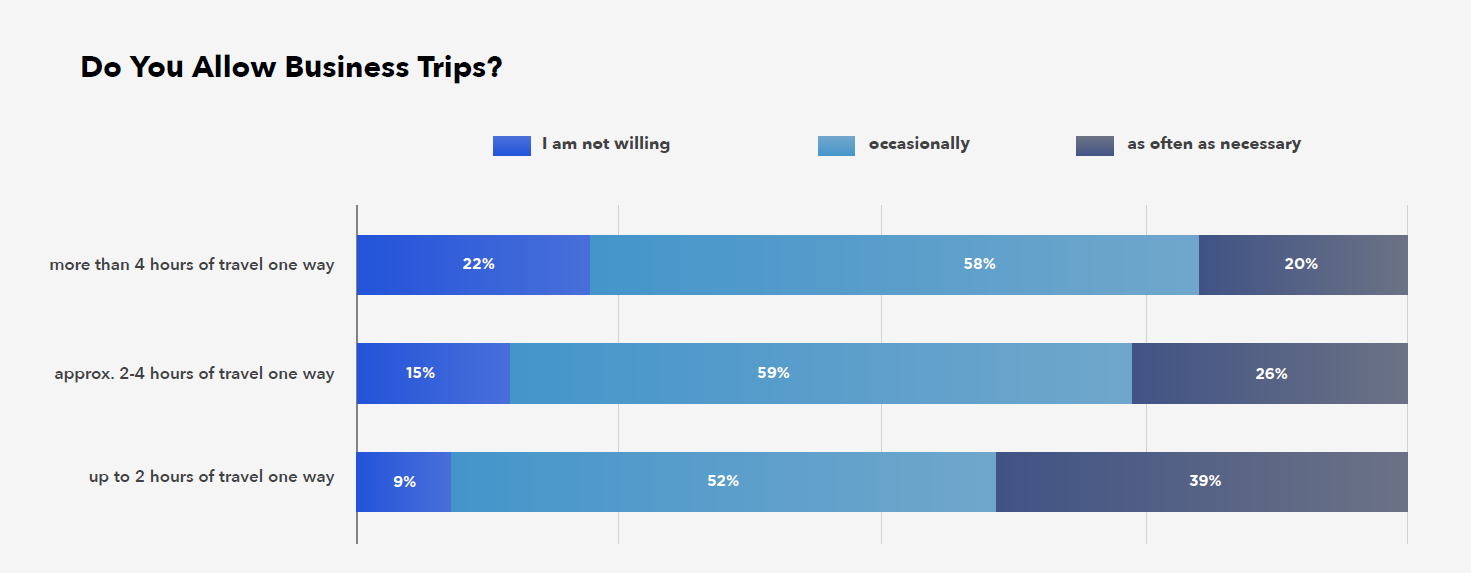
Consultants and developers are open to business travel – where the journey or flight takes up to 2 hours one way, and as many as 1/3 of specialists are ready to travel as often as necessary. Most voice an acceptance of travel, but only when it is really necessary.
Want to know more? Download the full SAP job market report, 2025.
DOWNLOAD REPORT



